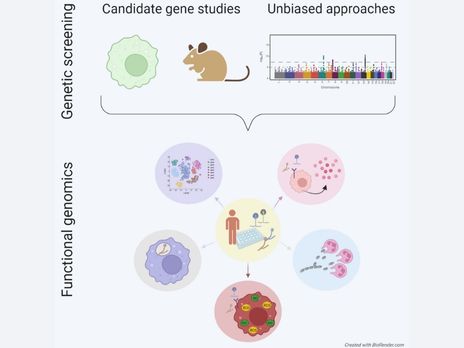
Scientific Highlights
Gonçales RA, Ricci-Azevedo R, Vieira VCS, Fernandes FF, Thomaz SMO, Carvalho A, Vendruscolo PE, Cunha C, Roque-Barreira MC, Rodrigues F. Paracoccin Overexpression in Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Enhances Fungal Virulence by Remodeling Chitin Properties of the Cell Wall. J Infect Dis. 2021 Jul 2;224(1):164-174. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa707; Steenwyk JL, Lind AL, Ries LNA, Dos Reis TF, Silva LP, Almeida F, Bastos RW, Fraga da Silva TFC, Bonato VLD, Pessoni AM, Rodrigues F, Raja HA, Knowles SL, Oberlies NH, Lagrou K, Goldman GH, Rokas A. Pathogenic Allodiploid Hybrids of Aspergillus Fungi. Curr Biol. 2020 Jul 6;30(13):2495-2507.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.04.071. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Ferreira BH, Ramírez-Prado JH, Neves GWP, Torrado E, Sampaio P, Felipe MSS, Vasconcelos AT, Goldman GH, Carvalho A, Cunha C, Lopes-Bezerra LM, Rodrigues F. Ploidy Determination in the Pathogenic Fungus Sporothrix spp. Front Microbiol. 2019 Feb 25;10:284. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00284. eCollection 2019. Lind AL, Wisecaver JH, Lameiras C, Wiemann P, Palmer JM, Keller NP, Rodrigues F, Goldman GH, Rokas A. Drivers of genetic diversity in secondary metabolic gene clusters within a fungal species. PLoS Biol. 2017 Nov 17;15(11):e2003583. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2003583. eCollection 2017 Nov.PMID: 29149178. Fernandes FF, Oliveira AF, Landgraf TN, Cunha C, Carvalho A, Vendruscolo PE, Gonçales RA, Almeida F, da Silva TA, Rodrigues F, Roque-Barreira MC. Impact of Paracoccin Gene Silencing on Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Virulence. mBio. 2017 Jul 18;8(4):e00537-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00537-17. Arts RJ, Novakovic B, Ter Horst R, Carvalho A, Bekkering S, Lachmandas E, Rodrigues F, Silvestre R, Cheng SC, Wang SY, Habibi E, Gonçalves LG, Mesquita I, Cunha C, van Laarhoven A, van de Veerdonk FL, Williams DL, van der Meer JW, Logie C, O’Neill LA, Dinarello CA, Riksen NP, van Crevel R, Clish C, Notebaart RA, Joosten LA, Stunnenberg HG, Xavier RJ, Netea MG. Glutaminolysis and Fumarate Accumulation Integrate Immunometabolic and Epigenetic Programs in Trained Immunity. Cell Metab. 2016 Dec 13;24(6):807-819. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.10.008. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Colabardini AC, Ries LN, Brown NA, Dos Reis TF, Savoldi M, Goldman MH, Menino JF, Rodrigues F, Goldman GH. Functional characterization of a xylose transporter in Aspergillus nidulans. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2014 Apr 1;7(1):46. doi: 10.1186/1754-6834-7-46. Menino JF, Almeida AJ, Rodrigues F. Gene knockdown in Paracoccidioides brasiliensis using antisense RNA. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;845:187-98. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-539-8_12. Almeida AJ, Cunha C, Carmona JA, Sampaio-Marques B, Carvalho A, Malavazi I, Steensma HY, Johnson DI, Leão C, Logarinho E, Goldman GH, Castro AG, Ludovico P, Rodrigues F. Cdc42p controls yeast-cell shape and virulence of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. Fungal Genet Biol. 2009 Dec;46(12):919-26. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2009.08.004. Epub 2009 Aug 15. Carvalho A, Pasqualotto AC, Pitzurra L, Romani L, Denning DW, Rodrigues F. Polymorphisms in toll-like receptor genes and susceptibility to pulmonary aspergillosis. J Infect Dis. 2008 Feb 15;197(4):618-21. doi: 10.1086/526500.